LCH (Light Combat Helicopter) is India’s first indigenous light combat helicopter developed by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL). LCH is built at the HAL facility in Bangalore.
The LCH is derived from the ALH (also known as Dhruv) and will carry the same weapons package now being qualified on board the armed Dhruv.
LCH will be armed with different types of weapons (among other guns, different types of missiles and rockets 70mm).
The LCH program has been started in 2003 to meet the operational requirements of both the air force and the army for close air support and anti-infantry and anti-armour role.
LCH is also equipped with a laser designator which makes this platform suitable for firing Thales SAL-Laser guided Rocket FZ275 LGR.
LCH armaments is equipped with 4 stub-wing mounted Forges de Zeebrugge built rocket launcher FZ231 carrying 70mm (2.75“) rockets.
The first LCH prototype (TD-1) made its maiden flight in March 2010. The second helicopter (TD-2) was showcased at the Aero India airshow in 2011.
The Indian Air Force (IAF) and Indian Army (IA) plan to procure 65 LCHs and 114 respectively. They are initially expected to begin entering service in 2012, but this was pushed back to due to developmental issues.
A 'certification of basic configuration' was issued on 16 October 2015.
HAL announced on 17 January 2019 that its Light Combat Helicopter (LCH) is “ready for operational induction” after completing all of its weapon integration tests.



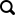

.jpg)